10 Essential Excel Functions Every Beginner Should Know
Share
Microsoft Excel is a powerful tool for managing and analysing data, but its true potential lies in its functions. Functions are predefined formulas that simplify complex calculations and save time. Whether you're a student, professional, or just someone looking to organise personal data, mastering these 10 essential Excel functions will make your life easier.
1. SUM
The SUM function adds up a range of numbers. It’s perfect for calculating totals, such as sales, expenses, or scores.
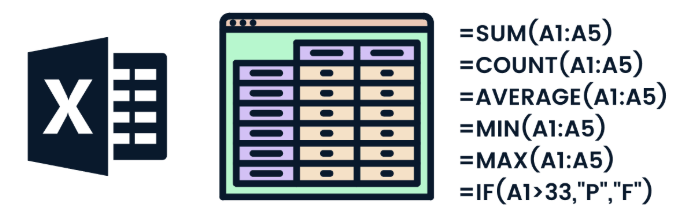
- Syntax: =SUM(range)
- Example: =SUM(B2:B4) adds all numbers in cells B2 through B4 (See Example below).
- Deep Dive: Learn more about the SUM function
2. AVERAGE
The AVERAGE function calculates the mean of a range of numbers. Use it to find the average score, temperature, or any other numerical data.
- Syntax: =AVERAGE(range)
- Example: =AVERAGE(B2:B4) calculates the average of values in cells B2 through B4 (See Example below).
- Deep Dive: Learn more about the AVERAGE function
3. IF
The IF function performs a logical test and returns one value if the condition is true and another if it’s false. It’s great for decision-making in your data.
- Syntax: =IF(condition, value_if_true, value_if_false)
- Example: =IF(B1>50, "Pass", "Fail") checks if the value in B1 is greater than 50 and returns "Pass" or "Fail."
- Deep Dive: Learn more about the IF function
4. VLOOKUP
The VLOOKUP function searches for a value in the first column of a table and returns a corresponding value from another column. It’s ideal for finding specific data in large datasets.
- Syntax: =VLOOKUP(lookup_value, table_range, column_number, [range_lookup])
- Example: =VLOOKUP("Apple", A:C, 2, FALSE) searches for "Apple" in column A and returns the corresponding value from column B. You can also choose a cell that has a value you are searching for (E2 instead of "Apple").
- Deep Dive: Learn more about the VLOOKUP function
5. COUNT
The COUNT function counts the number of cells in a range that contain numbers. Use it to tally numeric entries.
- Syntax: =COUNT(range)
- Example: =COUNT(B:B) counts how many cells in B column contain numbers.
- Deep Dive: Learn more about the COUNT function
6. MIN
The MIN function finds the smallest number in a range. It’s useful for identifying the lowest value in a dataset.
- Syntax: =MIN(range)
- Example: =MIN(B:B) returns the smallest number in B column .
- Deep Dive: Learn more about the MIN function
7. MAX
The MAX function finds the largest number in a range. It’s the opposite of MIN and helps identify the highest value.
- Syntax: =MAX(range)
- Example: =MAX(B:B) returns the largest number in B column.
- Deep Dive: Learn more about the MAX function
8. CONCATENATE (or CONCAT)
The CONCATENATE function combines text from multiple cells into one. It’s perfect for merging names, addresses, or other text data.
- Syntax: =CONCATENATE(text1, text2, ...)
- Example: =CONCATENATE(A3, " ", B3) combines the text inA3 andB3 with a space in between.
- Deep Dive: Learn more about the CONCATENATE function
9. LEFT and RIGHT
The LEFT and RIGHT functions extract a specific number of characters from the beginning (LEFT) or end (RIGHT) of a text string. They’re handy for parsing data.
- Syntax:
- =LEFT(text, number_of_characters)
- =RIGHT(text, number_of_characters)
- Examples:
- =LEFT(I1, 3) extracts the first 3 characters from the text in I1.
- =RIGHT(I1, 2) extracts the last 2 characters from the text in I1.
- Deep Dive: Learn more about the LEFT and RIGHT functions
10. TODAY
The TODAY function returns the current date. It’s useful for tracking deadlines, schedules, or any time-sensitive data.
- Syntax: =TODAY()
- Example: =TODAY() displays today’s date in the cell.
- Deep Dive: Learn more about the TODAY function
Why These Functions Matter
These 10 functions are the building blocks of Excel proficiency. By mastering them, you’ll be able to:
- Perform quick calculations.
- Analyze data efficiently.
- Automate repetitive tasks.
- Make informed decisions based on your data.
Visual Example
Here’s a simple table demonstrating some of these functions:
Take Your Excel Skills to the Next Level
If you found this guide helpful, imagine what you could achieve with hands-on case studies and advanced techniques! Download our comprehensive PDF course to master Excel with real-world examples and step-by-step tutorials.
👉 Buy the Excel Guide For Beginners Now
👉 Buy the Case Study to start Excel-ing
Conclusion
Excel functions are like tools in a toolbox—each has a specific purpose, and together they can solve almost any problem. Start practicing these 10 essential functions, and you’ll soon find yourself working faster and smarter in Excel. Happy spreadsheeting!







